The global regulatory environment has fundamentally redefined financial leadership, demanding that sustainability data meet the same standards of rigor and auditability applied to transactional finance. Modern CFOs face a compliance collision course where Dynamics 365 ESG reporting is not optional; it is a critical matter of financial risk and fiduciary duty. The global ESG Reporting Automation market reached USD 1.47 billion in 2024 and it is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 13.8% from 2025 to 2033, validating this urgent need for structured, scalable solutions. This new imperative requires you to fully integrate ESG into your core finance processes. This article will show you how MD365 can help you in automating your ESG reporting to achieve financial sustainability, and help you transform this compliance burden into a competitive advantage.
The Automation Gap: Why Manual Processes Fail Modern ESG Reporting
The regulatory shift means your current, fragmented approach to data collection is a direct threat to compliance. Global mandates like the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and the SEC’s focus on climate-related financial risk require material, auditable disclosures. Relying on outdated manual methods now leads directly to compliance failure.
The Compliance Collision Course: A Threat to Fiduciary Duty
Global regulators are forcing a merger between financial and non-financial reporting. The International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) S1 and S2 explicitly require sustainability information to be presented alongside financial statements, within the same official reporting package. This means your ESG data must possess financial-grade quality.
- The SEC and Materiality: While the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) climate rule faced a voluntary stay pending judicial review, the fundamental requirement for disclosing material climate-related financial risks and Scope 1 and Scope 2 GHG emissions remains the focus. Companies must collect and determine the materiality of climate data now to avoid risk.
- The CSRD Imperative: For multinational companies, compliance under the CSRD is often imminent and requires even more extensive disclosures and broader assurance over all sustainability data, not just emissions. Companies that build a high-assurance system for CSRD compliance are future-proofing their disclosures against most global mandates.
The High Cost of Fragmented Data and Siloed Systems
How much time does your team spend chasing data across disparate systems and local spreadsheets? The traditional approach, where data sits in silos across HR, procurement, and operations, is disastrously inadequate for the new standards.
- Auditability Risk is Paramount: Regulations now demand a clear, verifiable audit trail from the original source transaction (e.g., a flight booking) to the final calculated emission metric. Fragmented, spreadsheet-based data simply cannot provide the necessary governance, directly compromising the CFO’s ability to provide reliable public disclosures.
- Internal Governance Lags:Industry analysis confirms that 45% of surveyed companies have yet to establish the essential cross-functional groundwork required to fully integrate ESG data. Your finance team becomes an inefficient bottleneck, manually synthesizing data that should flow automatically from the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system.
- The Cost of Inefficiency: The manual collection and reporting process is deemed “obsolete and inefficient” by industry experts due to the accelerating complexity of global mandates. Automated solutions are necessary to reduce the risk of costly regulatory penalties and free up specialized finance resources.
This strategic pivot is already a top priority for executives. Enhancing Dynamics 365 ESG reporting and disclosures is a top initiative for CFOs, capturing their focus ahead of restructuring or general cost reduction. The sheer complexity and scope of new mandates are the primary drivers accelerating investment in automation.
How can you use Dynamics 365 for ESG reporting?
To meet the mandatory standards for data integrity and assurance, you must leverage the existing investment in your ERP system. Dynamics 365 Finance, integrated with the Microsoft Cloud for Sustainability, provides the architectural backbone necessary for continuous, auditable data management and a robust sustainability finance strategy.
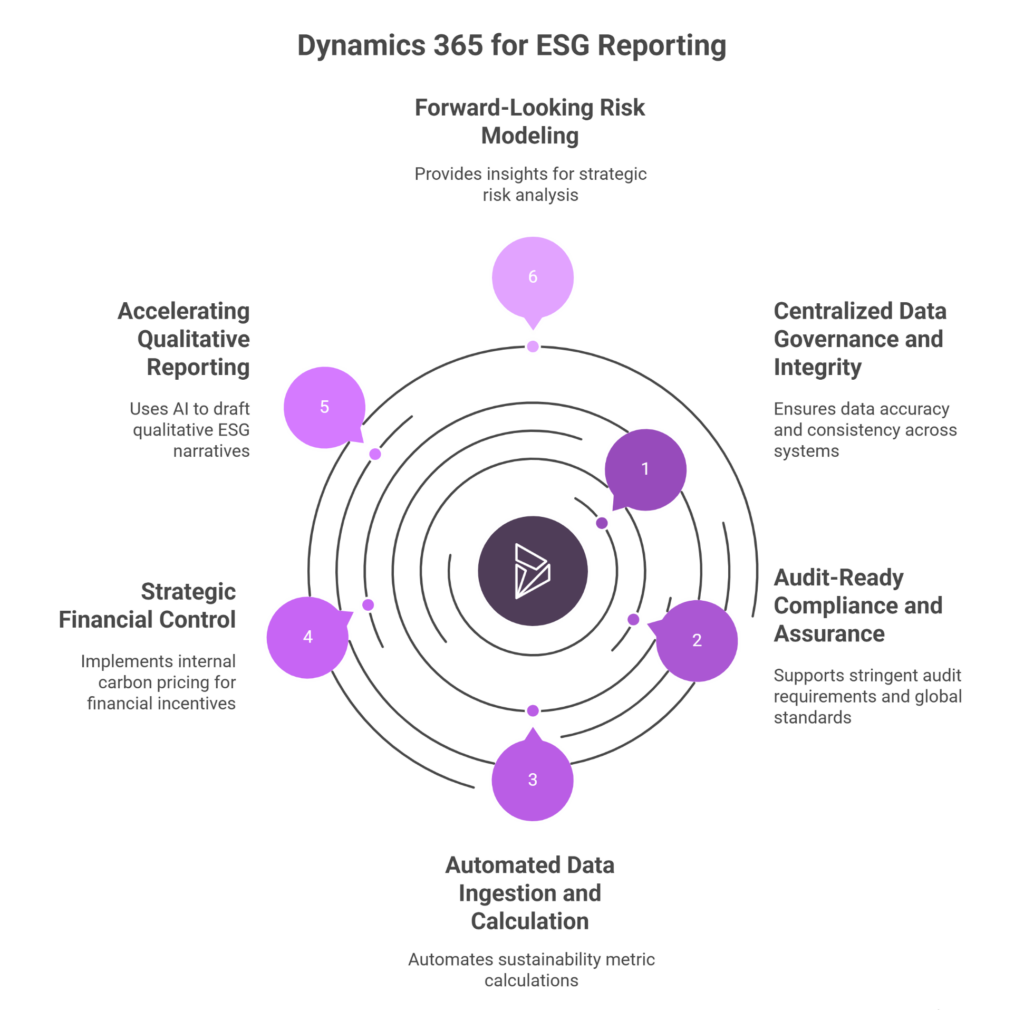
Here are six crucial ways Dynamics 365 enables financial-grade ESG reporting:
Centralized Data Governance and Integrity
Dynamics 365 Finance acts as the single source of truth for all transactional data required for ESG metrics, pulling crucial operational inputs from HR, procurement, travel, and IT systems. Centralizing this information is the foundational step toward breaking down data silos.
- Data Integration Architecture: The key technical mechanism is the integration between Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations apps and the Dataverse environment that hosts Microsoft Sustainability Manager (MSM). This connection ensures an auditable data chain from the source transaction to the calculated metric.
- Technical Enablement: To allow the two systems to communicate seamlessly and share data under a strict governance model, technical validation and configuration are required, including setting the Power Platform environment to enable user impersonation for finance and operations apps. This underscores that ESG reporting is now an integral IT project requiring enterprise-level governance.
- Enforced Collaboration: By automating the pulling of data directly from HR, finance, and IT systems, the D365 integration technically enforces the necessary cross-functional data collaboration that many organizations struggle to achieve manually.
Audit-Ready Compliance and Assurance
The system is designed from the ground up to support the stringent audit requirements of global mandates, particularly the CSRD and SEC rules.
- Double Materiality Alignment: Microsoft Sustainability Manager is preconfigured to support the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) frameworks, which mandate the analysis of double materiality. This principle requires reporting from two angles: the company’s impact on society/environment, and the impact of sustainability risks/opportunities on the company’s financial performance. This dual focus demands the seamless data integration provided by D365.
- Streamlined Audit Trails: MSM provides built-in audit-ready documentation, robust version control, and comprehensive reporting. This streamlined process significantly simplifies the complex, resource-intensive activity of obtaining third-party assurance.
- Framework Agnostic Reporting: The platform helps organizations align and report against various global standards, including CSRD, GRI, and IFRS, ensuring the data is structured consistently regardless of the required end format.
Automated Data Ingestion and Calculation
Moving beyond manual entries, Dynamics 365 uses automated tools to ingest, integrate, and calculate sustainability metrics from source systems.
- Data Standardization: MSM uses a mix of data ingestion methods to streamline the process, integrating data from systems with minimal manual effort and standardizing the input using the Microsoft for Sustainability data model.
- Accurate Emissions Calculation: The platform uses pre-built calculation methods that can be tailored to meet your specific needs, ensuring greater accuracy in tracking your environmental footprint across your entire operation and value chain.For example, emissions can be calculated and recorded directly from Purchase Documents or via formula-based entries using Sustainability Journals.
Strategic Financial Control: Internal Carbon Pricing
A core function of a modern sustainability finance strategy is internal carbon pricing, which embeds financial incentives directly into operational decision-making, altering capital allocation and project prioritization.
- Decentralized Accountability: Dynamics 365 allows you to set up and charge an internal fee for each unit of carbon or other greenhouse gas (GHG) emitted.Crucially, organizations can allocate these carbon fees by specific categories, including Country/regions and Responsibility Centers.
- Motivating Operational Change: By translating environmental impact into a specific, measurable cost tied to individual business unit performance, the system motivates managers to actively reduce their carbon footprint to save money This creates decentralized accountability across the organization.
- Financial Grade Tracking: These internal fees are automatically calculated when posting sustainability journals and posted directly to the Sustainability Ledger Entry page. This ensures that this internal pricing mechanism is subject to the same high level of control and auditability as traditional financial data.
Accelerating Qualitative Reporting with Copilot AI
ESG compliance requires both precise quantitative metrics and detailed qualitative narratives on strategy, risk oversight, and governance. Drafting these narratives, which involves synthesizing information across vast internal documentation and aligning it to complex regulatory phrasing, consumes significant resources.
- Intelligent Narrative Drafting:Copilot AI in Microsoft Sustainability Manager directly addresses this narrative burden. Utilizing large language models, Copilot helps users draft both qualitative and quantitative responses to fulfill disclosure requirements across standards like CSRD, GRI, and IFRS.
- Auditable Narrative Sources: The system allows users to upload organizational documentation. Copilot then finds the relevant data within those documents and suggests how to write facts that meet the specific disclosure requirements with references to the source documentation.
- Efficiency Gain: This capability saves time and effort by synthesizing large amounts of internal data into a comprehensive, auditable response, thereby accelerating the ability to draft complex disclosure requirements.
Forward-Looking Risk Modeling and Scenario Planning
The automated, high-quality data flow from D365 Finance to Microsoft Sustainability Manager provides the real-time insights needed for strategic analysis, transforming compliance data into a forward-looking management tool.
- KPI Visualization: The platform utilizes Power BI templates that align with the ESG data models to accelerate the visualization of applicable metrics and the generation of streamlined, insights-driven reports.
- Integrated Risk Assessment: Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management embeds Power BI reports directly into the Supply Risk Assessment workspace. These tools allow finance analysts to analyze calculated risks for planned purchases and identify high-risk product segments.
- Strategic Scenario Modeling: By filtering the integrated risk and performance reports, organizations can prevent unwanted double accounting of planned orders and focus on the top-10 products ranked by aggregated risk, enabling proactive modeling of material supply chain and climate risks.
|
Focus Area |
How Dynamics 365 Enables It? |
Strategic Business Impact |
|
Centralized Data Governance and Integrity |
Dynamics 365 Finance acts as the single source of truth for ESG-related data across HR, procurement, and IT systems, integrated through Dataverse and Microsoft Sustainability Manager. |
Eliminates data silos and ensures full traceability from source transactions to ESG metrics. |
|
Audit-Ready Compliance and Assurance |
Supports CSRD, ESRS, and SEC compliance using Microsoft Sustainability Manager’s standardized frameworks and documentation tools. | Simplifies third-party assurance and ensures consistent, audit-ready reporting. |
| Automated Data Ingestion and Calculation | Automates sustainability data collection and emission calculations using standardized models across connected systems. |
Reduces manual work, increases accuracy, and enables real-time ESG data updates. |
|
Internal Carbon Pricing and Accountability |
Embeds internal carbon pricing within D365 Finance to allocate GHG fees by region or responsibility center. | Promotes decentralized accountability and drives emission reduction through cost visibility. |
| AI-Powered Qualitative Reporting | Uses Copilot in Microsoft Sustainability Manager to generate disclosure narratives with source-linked references. |
Accelerates ESG report preparation and maintains audit-ready accuracy. |
|
Risk Modeling and Scenario Planning |
Combines Power BI and D365 Supply Chain data to analyze climate and supply chain risks. |
Enables proactive decision-making and scenario-based planning for resilience. |
A CFO’s Roadmap: Steps to Implement ESG Reporting in D365
Implementing automated Dynamics 365 ESG reporting is a business transformation project that requires a structured, phased approach to ensure success, data quality, and long-term strategic value.
Phase 1: Assess, Define, and Secure Governance
The initial phase focuses on preparation and strategic alignment, laying the foundation of high-quality data.
- Define ESG Goals and KPIs: Align business objectives with measurable, quantifiable ESG Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). This translates abstract goals into targets you can track within the D365 system. This requires clear targets aligned to corporate strategy.
- Conduct Readiness Assessment: Identify existing data silos, review current manual data collection processes, and define the operational baseline. This step determines the scope of necessary automation.
- Establish Data Governance: Secure cross-functional commitment for ESG reporting. Leverage D365 tools for materiality mapping to prioritize the ESG topics most relevant to your sector and size, focusing resources where financial and environmental impact converge.
Phase 2: Design, Integrate, and Automate
This phase translates the strategy into technical execution, building the core of your automated system.
- Architectural Integration: Design and configure the Dataverse connection to seamlessly link source data within D365 Finance (HR, procurement, operations) with Microsoft Sustainability Manager. This ensures automated data collection occurs with minimal manual effort.
- Configure Calculations: Implement and tailor the pre-built calculation methods within MSM for accurate emissions and metric generation. Ensure all required emission factors are correctly applied (e.g., converting to CO₂ equivalent).
- Develop Dashboards and Reports: Build custom ESG dashboards using Power BI templates to visualize real-time progress against the defined KPIs and accelerate the creation of streamlined reports.
Phase 3: Optimize, Govern, and Reinforce
The final phase ensures the platform delivers continuous strategic improvement and maintains long-term adoption.
- Automate Workflows and Alerts: Configure automated workflows for ESG compliance and reporting, utilizing real-time feedback loops and automated alerts within the system.
- Continuous Risk Modeling: Actively leverage the integrated D365 tools for continuous scenario planning, modeling exposure to climate and operational risks using supply chain reports.
- Sustain Adoption and Audit Readiness: Maintain streamlined audit trails, version control, and documentation for recurring third-party assurance. Provide role-based training and governance documentation to equip and enable all finance users to adopt the new D365 processes.
Conclusion
The era of fragmented, manually managed ESG data is over. Global regulatory pressures demand the integration of sustainability metrics into the core financial function. By leveraging Microsoft Sustainability Manager and Power Platform, you can transform your compliance process into a strategic accelerator.
Implementing robust Dynamics 365 ESG reporting ensures your data is not only complete and accurate but also future-proofed against evolving global assurance requirements. This strategic move effectively embeds sustainability into core sustainability finance mechanisms, driving capital efficiency through advanced features like internal carbon pricing and proactive risk modeling.
Ready to transform your ESG data from a compliance headache into a strategic asset? Partner with industry leaders. Visit Folio3 Dynamics today to explore expert Dynamics 365 implementation services tailored to unlock your full sustainability potential and ensure audit readiness.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use Microsoft Fabric’s ESG metrics instead of Microsoft Sustainability Manager with D365?
Yes, it’s possible to use Microsoft Fabric’s ESG metrics by ingesting data into its Lakehouse architecture and mapping to the ESG schema. But doing so requires manually building transformation logic and schema alignment, whereas MSM handles much of that integration and auditability out of the box.
Q2: How reliable is AI/ChatGPT for drafting ESG disclosures based on standards like IFRS S2?
Many professionals experiment with AI prompts to automate disclosures, but caution remains because AI outputs require human review and validation to ensure compliance and factual accuracy.
Q3: When migrating reporting into D365/Dataverse, how do you replicate custom SSRS or legacy reports that used direct SQL queries?
Because production D365 instances typically block direct SQL access, many resolve this by exporting data to Azure Data Lake or using BYOD (Bring Your Own Database) to recreate reporting sources, or by re-implementing reports using Power BI / Dataverse queries.
Q4: What ESG reporting software do organizations often compare when evaluating Microsoft’s ecosystem?
Users often evaluate solutions like Workiva, Sphera, Watershed, and Envizi for data aggregation, calculation, and disclosure, comparing them against Microsoft’s integrated offering in terms of cost, ease of deployment, and framework support.
Q5: What skillset do people entering ESG / sustainability reporting need now?
Practitioners emphasize that a mix of quantitative skills (Excel, data modeling, benchmarking), qualitative/reporting skills (narrative writing, framework understanding), and familiarity with ESG standards (e.g. GRI, CSRD) are essential.
Q6: Does ESG reporting truly deliver societal value, or is it mostly greenwashing?
Many see ESG reporting as a crucial tool for transparency and accountability, driving positive behavior in companies; while it can be misused for marketing, stronger regulation and auditability reduce the risk of superficial claims.